Integrate OpenCover with Azure DevOps
OpenCover is a code coverage tool that measures both branch and sequence points for a given .Net application. In my case, I wanted to measure code coverage of a .Net web API project. The idea is to start OpenCover, run end-2-end tests (or other tests invoking my API) and generate a coverage file. This setup gives you insight into how much of your API is covered by, for example, end-2-end tests.
 Photo by Kai Dahms on Unsplash
Photo by Kai Dahms on Unsplash
To achieve this, I use OpenCover.Console.exe and attach it to the IIS process of the backend application as described in the wiki of OpenCover. This works fine for manually starting OpenCover, but in my Azure DevOps pipeline everything should be automated. To do so, I created three PowerShell scripts. One to start OpenCover, one to Invoke the start script on another machine and one to close OpenCover and generate a report.
Starting OpenCover
The start script stops the current running backend IIS application. After it is stopped the actual OpenCover.Console.exe can be started:
OpenCover.Console.exe -target:C:\Windows\System32\inetsrv\w3wp.exe -targetargs:-debug -targetdir:C:\iisprojectdir -output:C:\reports\opencover-result.xml -filter:+[*]* -register:user Once this is completed the backend application is running again and can be used for testing. In the Task Manager you will now find two processes for the same application. It might be useful to perform some warmup for the new running instance of your application.
Starting OpenCover should not be done with remote PowerShell. Remote PowerShell will start a session, start OpenCover and when the task is finished it will close the session. When the PowerShell session is ended OpenCover will be killed. This can be avoided by using Invoke-Command instead with the -InDisconnectedSession parameter:
Invoke-Command -ComputerName $server -Credential $credential -InDisconnectedSession -ScriptBlock { <Insert OpenCover Start script> }Note: Be aware that the application will be running as the user running the script.
Stopping OpenCover
After testing is done it’s important to not end the OpenCover process itself but the new w3wp process. If the OpenCover process is ended first no coverage file will be generated after it. Unfortunately, it’s not easy to find this process since OpenCover doesn’t return any information about that process. To find the process any way we can use Get-WmiObject to get a process based on a name and command line. In this case the start script used the CommandLine “C:\Windows\System32\inetsrv\w3wp.exe” -debug So in the second script the right w3wp process is searched for and when found the process gets killed. Now OpenCover will generate the coverage file after a couple of seconds. In the end the backend IIS application can be started again in IIS like it was initially running.
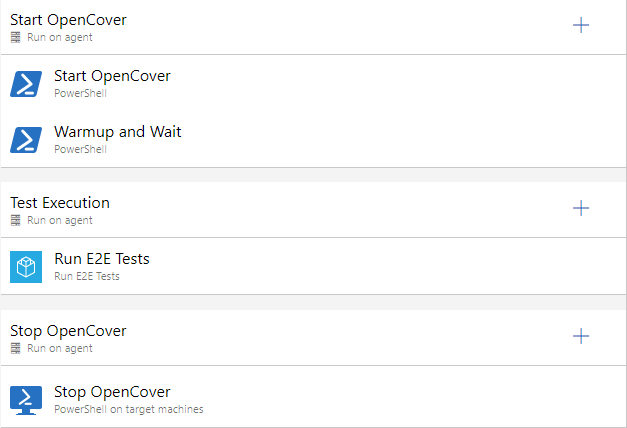
Pipeline
Both scripts can be used inside an Azure DevOps pipeline with a test execution in between. When OpenCover is stopped correctly, the generated result(xml) can be used for reporting. More about this subject will be covered in my next post. Stay tuned!
The scripts can be found on my GitHub. Feel free to ask questions!
